An Presentation to the Hominal Body
Structural Formation of the Human Trunk
Eruditeness Objectives
By the end of this subdivision, you will be able to:
- Account the structure of the earthborn torso in price of cardinal levels of organization
- Name the eleven electric organ systems of the human body and identify leastways incomparable organ and cardinal major function of each
Before you begin to study the different structures and functions of the form, it is accommodating to consider its BASIC computer architecture; that is, how its smallest parts are assembled into larger structures. It is accessible to consider the structures of the body in terms of fundamental levels of organization that increase in complexness: microscopical particles, atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, variety meat, organ systems, organisms and biosphere ((Figure)).
Levels of Structural Organization of the Human Trunk
The organization of the body oftentimes is discussed in damage of six distinct levels of flaring complexness, from the smallest material building blocks to a unique human organism.
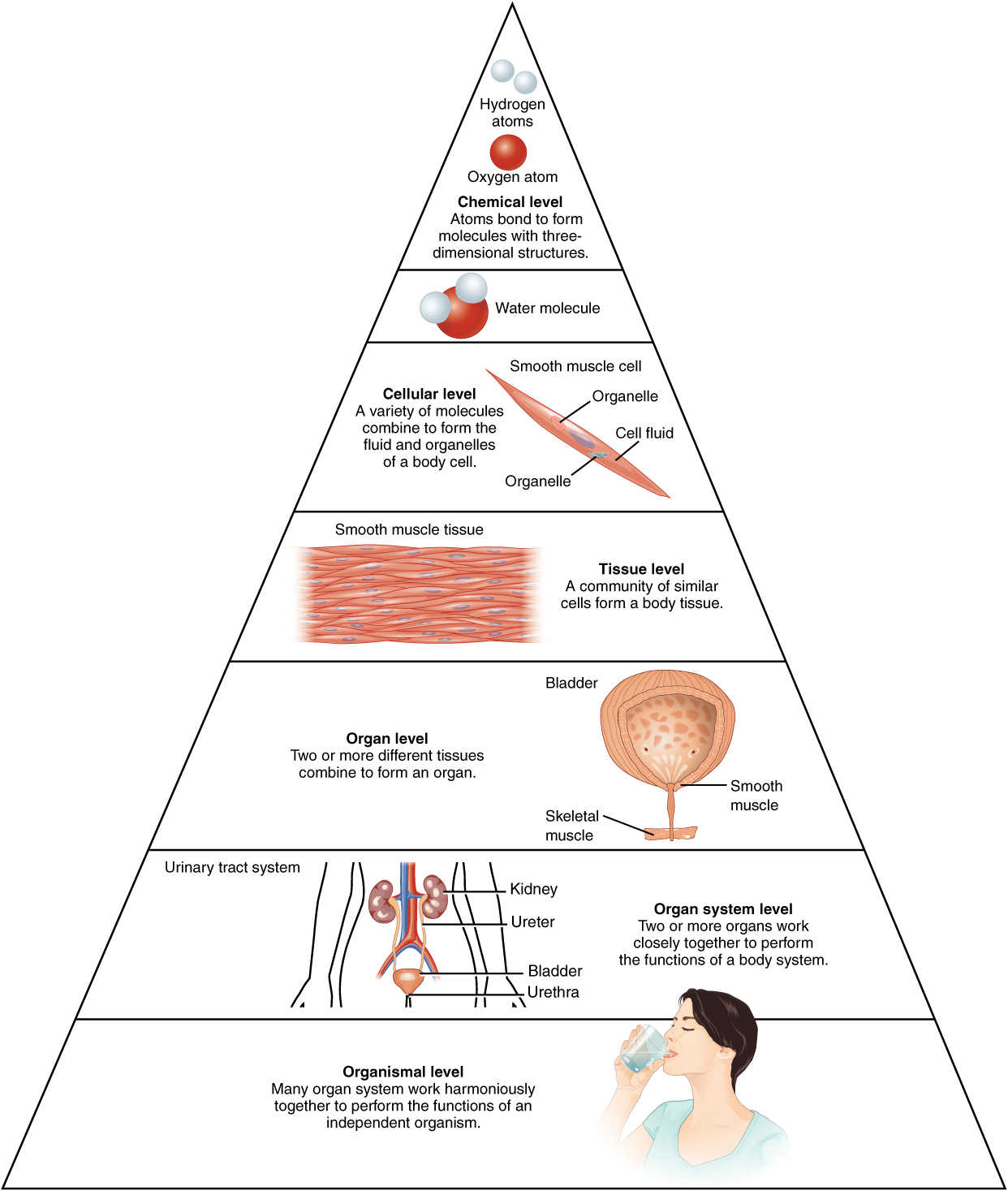
The Levels of Organization
To study the chemical level of organization, scientists study the simplest edifice blocks of affair: microscopical particles, atoms and molecules. All matter in the universe is composed of one or more unique pure substances called elements, familiar examples of which are hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, atomic number 20, and iron. The smallest social unit of some of these staring substances (elements) is an atom. Atoms are made up of subatomic particles much as the proton, negatron and neutron. Two or more atoms combine to form a molecule, such as the water molecules, proteins, and sugars found in sustenance things. Molecules are the chemical substance building blocks of all body structures.
A cell is the smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism. Even bacteria, which are extremely small, severally-living organisms, have a cellular structure. To each one bacterium is a single cell. All living structures of human anatomy contain cells, and almost all functions of human physiology are performed in cells operating theatre are initiated by cells.
A human cell typically consists of negotiable membranes that hold in cytoplasm, a water-based cellular fluid together with a variety of diminutive functioning units called organelles. In human race, A all told organisms, cells perform all functions of life. A tissue is a group of many similar cells (though sometimes self-possessed of a few related types) that work jointly to perform a specific function. An harmonium is an anatomically distinct structure of the body composed of two or more tissue types. Each organ performs one or more specific physiologic functions. An organ system is a group of organs that work jointly to do major functions or meet physical needs of the body.
This book covers eleven distinct organ systems in the human body ((Figure) and (Figure)). Assignment organs to reed organ systems fanny be imprecise since variety meat that "lie" to matchless system can also have functions integral to another organization. In fact, most organs contribute to more than one system.
Organ Systems of the Chassis
Organs that work together are grouped into pipe organ systems.
.jpg#fixme)
Organ Systems of the Human Body (continued)
Organs that work together are grouped into organ systems.
.jpg#fixme)
The organism level is the highest level of organization. An organism is a living being that has a cellular structure and that lavatory independently do all physiologic functions necessary for life. In multicellular organisms, including humans, all cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems of the body do work together to hold out the life and wellness of the organism.
Chapter Review
Life processes of the soma are maintained at single levels of structural organization. These include the chemical, cellular, tissue, harmonium, electronic organ arrangement, and the being level. Higher levels of constitution are built from lower levels. Hence, molecules combine to form cells, cells combine to form tissues, tissues corporate trust to form organs, organs flux to form organ systems, and organ systems combine to form organisms.
Review Questions
The smallest independently functioning building block of an organism is a(n) ________.
- cell
- molecule
- Hammond organ
- weave
A compendium of similar tissues that performs a specific function is an ________.
- organ
- organelle
- organism
- organ system
The body system responsible structural support and apparent motion is the ________.
- cardiovascular system
- endocrine system
- athletic organization
- skeletal system
Acute THINKING QUESTIONS
Name the six levels of formation of the fallible body.
Material, cellular, tissue, organ, organ organization, being.
The female ovaries and the male testes are a part with of which trunk system? Can these organs be members of more than one pipe organ system? Why Beaver State why not?
The female ovaries and the manful testes are parts of the reproductive system. But they also secrete hormones, as does the endocrine system, therefore ovaries and testes function within both the endocrine and reproductive systems.
Glossary
- cell
- smallest severally functioning unit of all organisms; in animals, a cell contains cytoplasm, equanimous of graceful and organelles
- organ
- functionally distinct structure self-possessed of ii or more types of tissues
- organ system
- group of variety meat that bring up together to contain out a particular proposition operate
- being
- living being that has a living thing structure and that can independently perform every physiologic functions necessary for living
- tissue
- radical of analogous or closely affiliated cells that act together to perform a particularized function
groups of similar cells that perform specific tasks makeup
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/anatomyandphysiologyopenstax/chapter/structural-organization-of-the-human-body/

0 Komentar